Showing posts with label Passive Remote Sensing. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Passive Remote Sensing. Show all posts
Tuesday, 29 April 2014
Thursday, 20 March 2014
What Is Open Source Remote Sensing ?
 |
| Open Source Remote Sensing |
Remote sensing is defined as a technology which provides information about the environment or the phenomenon on the earth's surface which is far away or remotely sensed. A person can get information about the things without any direct as well as physical contact with an object.
Open source remote sensing is a software with a source code which is available for all as a source to learn, to explore and to make use of it. Open sources are the licensed softwares made by many people which are freely available and can be easily used and further modified by anyone for the credits.
SOME SOURCES OF REMOTE SENSING:
IDRISI
Erdas
ENVI
ILWIS
QGIS
Orfeo Toolbox
R
GRASS
SAGA GIS
The above given sources of remote sensing some are free whereas few are not.
ILWI,QGIS for GIS, Orfeo toolbar, R,GRASS,SAGA are some of the free or open sources for remote sensing whereas IDRISI,Erdas,ENVI are not free.
Ques. How open source software is useful?
Ans. It is enourmously useful to the people who even have a little knowledge about this. It is available free of cost with license that means it avoids expense. It can be used by anyone and can also be further modified for the credits.
Ques. What are the objectives of open source?
Ans. There are many objectives like:
- People who are new to this field can gain knowledge about this and is also theoretically beneficial to them.
- Through this open source lectures can be delivered to the students in the lab.
- The changes can be made in the software and can be generated further.
- It can be very helpful for the research scholars to carry out their research in a good and technical manner.
Ques. What are the best open source for remote sensing?
Ans. The best open source for remote sensing are QGIS 2.0.1 "Dufour",GDAL 1.9.2, GRASS GIS 6.4.3,Orfeo Toolbox 3.18, R 3.0.2 and SAGA 2.1.
Ques. What are the microsoft windows in which open source can run?
Ans. Linux, windows, windows Vista, windows Azure, etc are some of the microsoft windows that support open sources and the applications like JAVA and C++ makes the software easily run.
Thursday, 21 November 2013
Passive Remote sensing
So far, we have
read various definitions and descriptions of Remote Sensing. But only
an appropriate definition would make the very concept of Remote
Sensing clear. Remote Sensing is the acquisition of information about
an object or phenomenon relating to the object without making any
kind of physical contact with the object.
Passive remote
sensing is a class of Remote Sensing that make use of Passive Remote
Sensors. The sensors are used to detect natural radiations that are
emitted by the object or by its surrounding areas. The most common
source of energy that is measured by Passive Remote Sensors is
“Reflected Sunlight”.
The sensors that
are used for Passive Remote Sensing can only be used when there is
some naturally occurring energy available. Thus, for all reflected
energy, Passive Remote Sensing can only take place when the sun is
illuminating the surface of the earth. No reflected is available from
the sun at night.
Passive Remote
Sensors obtain measurements from naturally occurring radiations. The
sensors have several characteristics and they are often called its
advantages :
- Multiple wavelength information
- Comparatively low electrical power requirements
- Small size possible
The Passive Remote
Sensing systems are pretty much similar to what the eyes see. They
are more or less similar to photographs. Passive Sensing radiates
visible light. Some of the very common examples of Passive Remote
Sensing are :
- Charge-Coupled Devices
- Infrared
- Film Photography
- Radiometers
The energy that is
radiated naturally can be detected day or night, as long as the
amount of energy is large enough to be recorded.
Monday, 18 November 2013
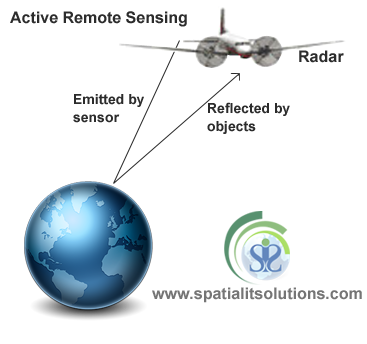
Active Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing refers to the acquisition of information about an object without touching it. In modern usage, Remote Sensing makes use of aerial sensor technology to detect and classify objects. The aerial sensors detect objects both on the surface of the earth and in the atmosphere by means of propagating signals. These signals are electromagnetic radiations that are emitted by aircraft and satellites.
Active Remote Sensing is a class of remote Sensing that makes use of Active Remote Sensors. These sensors provide their own source of illumination and they emit radiations that are directed towards the target body that is to be investigated. Active Remote sensors emit energy in order to scan the objects and areas and they then detect and measure the radiations that are reflected or are backscattered from the target body.
The sensors transmit short pulses of the electromagnetic energy in the direction of the target and they record the origin and strength of the reflected rays received from the object within the system's field of view.
An active Remote Sensing System is not dependent on the sun's rays or the thermal properties of the earth. However the system requires a fairly large amount of energy to illuminate the target body. The sensors that are used in this system create their own electromagnetic energy that
The sensors transmit short pulses of the electromagnetic energy in the direction of the target and they record the origin and strength of the reflected rays received from the object within the system's field of view.
An active Remote Sensing System is not dependent on the sun's rays or the thermal properties of the earth. However the system requires a fairly large amount of energy to illuminate the target body. The sensors that are used in this system create their own electromagnetic energy that
- Is transmitted from the sensor towards the contour
- Interacts with the contour and produces reflected rays
- Is recorded in the remote sensor's receiver
The advantages of Active Remote Sensing are :
- Ability to take measurements regardless of the time of the day or the season.
- Easy to examine the wavelength of the radiations that are not provided by the sun.
Active remote sensors can be used to observe the earth's surface even when the sky is covered with clouds. This is because they rely on their own source of radiation to illuminate the object. This is done so that the energy radiated and reflected to the sensors is measured.
The most common type of sensor that are used for Active Remote Sensing is a “RADAR”. Another example of an active remote sensor is LiDAR. They measure the time delay between the emission and return to establish the location, direction and speed of the object.
Friday, 15 November 2013
Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing is the technique that is used for obtaining information about objects by analyzing the data that is collected by special instruments that do not have any physical contact with the object/s under investigation.
Alternatively, it can be termed as acquiring the salient information of an object or aspect without the need to physically touch it. The technique generally makes use of aerial sensor technologies that detect or classify the objects on earth by means of electromagnetic radiations that are emitted by aircraft or satellites. The two main components of remote Sensing are “Data Capture” and “Data Analysis”.
Alternatively, it can be termed as acquiring the salient information of an object or aspect without the need to physically touch it. The technique generally makes use of aerial sensor technologies that detect or classify the objects on earth by means of electromagnetic radiations that are emitted by aircraft or satellites. The two main components of remote Sensing are “Data Capture” and “Data Analysis”.
 |
| Remote Sensing |
Remote Sensing is broadly categorized into two main types:
Active Remote Sensing
Passive Remote Sensing
In Passive Remote Sensing passive sensors are able to detect the natural radiations that are emitted by objects and their surrounding areas. They respond to external stimuli. Reflected sunlight is the most common source of radiation that is measured by passive sensors. Charge-coupled devices, infrared and radiometers are some examples of passive sensors.
As the name also suggests in Active Remote Sensing Active sensors are used to measure the radiations that are reflected back from the target bodies. They respond to internal stimuli. RADAR is a common example of active remote sensing technique. A RADAR measures the time delay between the emission and return of a radiation, based on which it calculates the location, speed and the direction of an object.
Following are the application areas for Remote Sensing technology:
Ocean Applications: The technique of remote Sensing can also be used to monitor ocean circulation and current system. It is also used to measure ocean temperature and the wave heights. Remote sensing can also be used to track sea ice or in cases where you want to get a better understanding of the oceans and manage ocean resources.
Hazard Assessment: It has its importance when there is a need to track hurricanes, earthquakes, erosion, and floods and other natural disasters. The data that is given can be used to assess the effects of natural disasters. Based on the data that is obtained by Remote Sensors some strategies can be made that can be used before and after the disaster.
 |
| Hazard Assessment |
Coastal Applications: Remote Sensing is used to monitor the changes that occur on the shoreline or even in the case of tracking sediment transport etc. The data that is obtained by Remote Sensing can also be used for coastal mapping and for preventing erosion.
The complete remote sensing process can be summarized as follows:
The data is captured by the Remote Sensors, such information is recorded and then analyzed by some interpretive and measurement techniques. This is done in order to provide useful information about the objects that are under investigation. The techniques are diverse and vary from the traditional methods of visual interpretation to the methods using computer processing.
More Knowledge Contact :- Spatial IT Solutions
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)